Condition
Pediatric Ewing Sarcoma
Key points about Ewing sarcoma
- Ewing sarcoma is a rare group of cancers that usually occur in the bone, but can also occur in soft tissue.
- X-ray and other imaging tests may be used in diagnosing Ewing sarcoma. A biopsy is needed to make a definite diagnosis.
- Ewing sarcoma is treated with chemotherapy followed by surgery and/or radiation therapy. High-dose chemotherapy and stem cell transplant may be used in some children.
- Continuous follow-up care during and after treatment is necessary.
- Many complications can occur from the cancer and from the treatment. The complications may be short- or long-term.
Schedule an Appointment
Our pediatric specialists provide personalized care for your child’s physical, mental and emotional health needs. Meet our providers and schedule an appointment today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Ewing sarcoma?
What causes Ewing sarcoma in children?
What are the symptoms of Ewing sarcoma in children?
How is Ewing sarcoma in children diagnosed?
What are possible complications of Ewing sarcoma in children?
How is Ewing sarcoma in children treated?
How can I help my child live with Ewing sarcoma?
When should I call my child’s healthcare provider?
Meet the Providers Who Treat Ewing Sarcoma
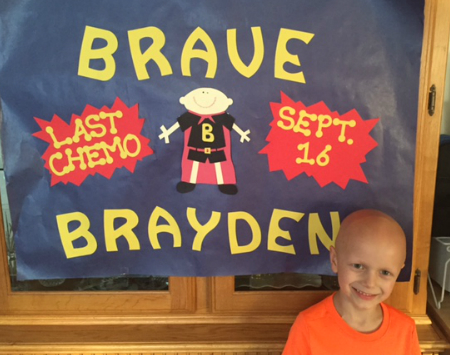
Brayden's Story
From the outside, Brayden Schofield seems like a regular six-year-old boy who loves sharks, snakes, and playing with his little brother. But what most people don't know is that Brayden's life – and left arm – was saved by a rare bone tumor surgery performed by a team of doctors at Children's National Hospital.
Departments that Treat Ewing Sarcoma

Oncology
The Oncology Program at Children's National is ranked one of the best cancer centers for children by U.S. News & World Report thanks to our high level of experience and expertise. Learn more about this program.

Help Kids and Make a Difference
Invest in future cures for some of life's most devastating diseases. Give today to help more children grow up stronger.