
Burn Surgery
Conditions

Children's National Burn Surgery team members treat a variety of burns, and offer the best care possible to children as they recover from burn injuries. Learn more about the conditions we treat below.
Burn Types
There are three types of burns. The type of burn and how it was caused will decide the treatment.
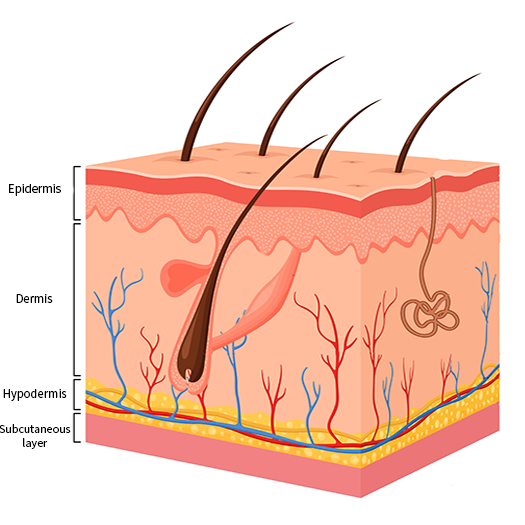
Superficial
- Only the top layer of the skin called the epidermis is hurt.
- These burns are pink or red.
- First degree burns are painful, and dry (like a sunburn).
- There are no blisters.
- Superficial burns heal in 3-7 days with no scarring.
Partial Thickness
- The epidermis (top layer of the skin) and the dermis (second layer of skin) are injured.
- Second degree burns are painful and will have blisters.
- Some second degree burns heal within 2-3 weeks without leaving a scar.
- Some partial thickness burns take 2-6 weeks to heal and may require a skin graft.
Full Thickness
- This burn includes all the layers of the skin (the entire dermis).
- These burns make the skin look shiny (waxy) and white. This is the most serious type of burn.
- Full thickness burns often require a skin graft and often take at least 3-6 weeks to heal.
Conditions We Treat
Burns are painful wounds caused by thermal, cold, electrical, chemical or electromagnetic energy. Smoking and open flame are the leading causes of burn injury in adults. Scalding is the leading cause of burn injury in children. Learn more about the types of pediatric burns we treat.






